24K Learn about accretion theory. Study the accretion definition, discover the many processes of planetary accretion, examine current models like the core accretion theory, and identify
Condensation vs Polycondensation: Meaning And Differences
The condensation sequence is the sequence by which different kinds of material condense out of the solar nebula based on the distance from the sun and decreasing temperature.

Source Image: science.org
Download Image
Oct 5, 2022What is the difference between accretion and condensation? The water molecules cling to the object and then changes from a water vapor into liquid water on an object which makes the object moist. The moisture is called condensation. Accretion is when there is a slow increase in size of an object as matter builds up due to gravity.

Source Image: science.org
Download Image
Applied Sciences | Free Full-Text | A New Ice Accretion Model for Aircraft Icing Based on Phase-Field Method Nov 21, 2023Accretion is the gradual accumulation of solid materials due to gravitational forces.In the accretion process, gas and dust are attracted by gravitational forces to form a central collection of
Source Image: cambridge.org
Download Image
What Is The Difference Between Condensation And Accretion
Nov 21, 2023Accretion is the gradual accumulation of solid materials due to gravitational forces.In the accretion process, gas and dust are attracted by gravitational forces to form a central collection of What is the difference between condensation and accretion? Solution Summary: The author explains the difference between condensation and accretion. Condensation is the first process of planet formation where solid grains are formed depending on the temperature of the region.
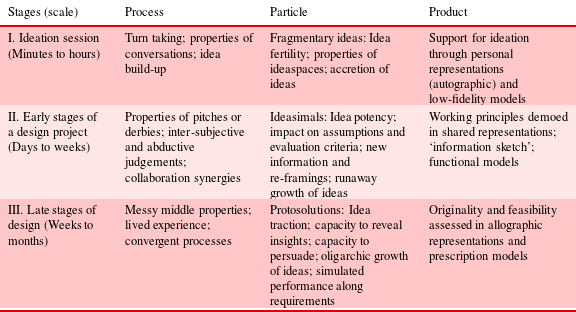
Accretion theory of ideation: evaluation regimes for ideation stages | Design Science | Cambridge Core
Earth builds up first from cooling materials (initially hot and then cool). This requires a very rapid build up of earth, perhaps within 10,000 yrs of the initiation of condensation. Density control. Temperature control. The early core of the earth contains the refractory elements/early condensates. IB Astronomy 2.1 Origin of the Solar System Diagram | Quizlet

Source Image: quizlet.com
Download Image
Types Of Accretion And Their Efficiency Rates – FasterCapital Earth builds up first from cooling materials (initially hot and then cool). This requires a very rapid build up of earth, perhaps within 10,000 yrs of the initiation of condensation. Density control. Temperature control. The early core of the earth contains the refractory elements/early condensates.

Source Image: fastercapital.com
Download Image
Condensation vs Polycondensation: Meaning And Differences 24K Learn about accretion theory. Study the accretion definition, discover the many processes of planetary accretion, examine current models like the core accretion theory, and identify
Source Image: thecontentauthority.com
Download Image
Applied Sciences | Free Full-Text | A New Ice Accretion Model for Aircraft Icing Based on Phase-Field Method Oct 5, 2022What is the difference between accretion and condensation? The water molecules cling to the object and then changes from a water vapor into liquid water on an object which makes the object moist. The moisture is called condensation. Accretion is when there is a slow increase in size of an object as matter builds up due to gravity.
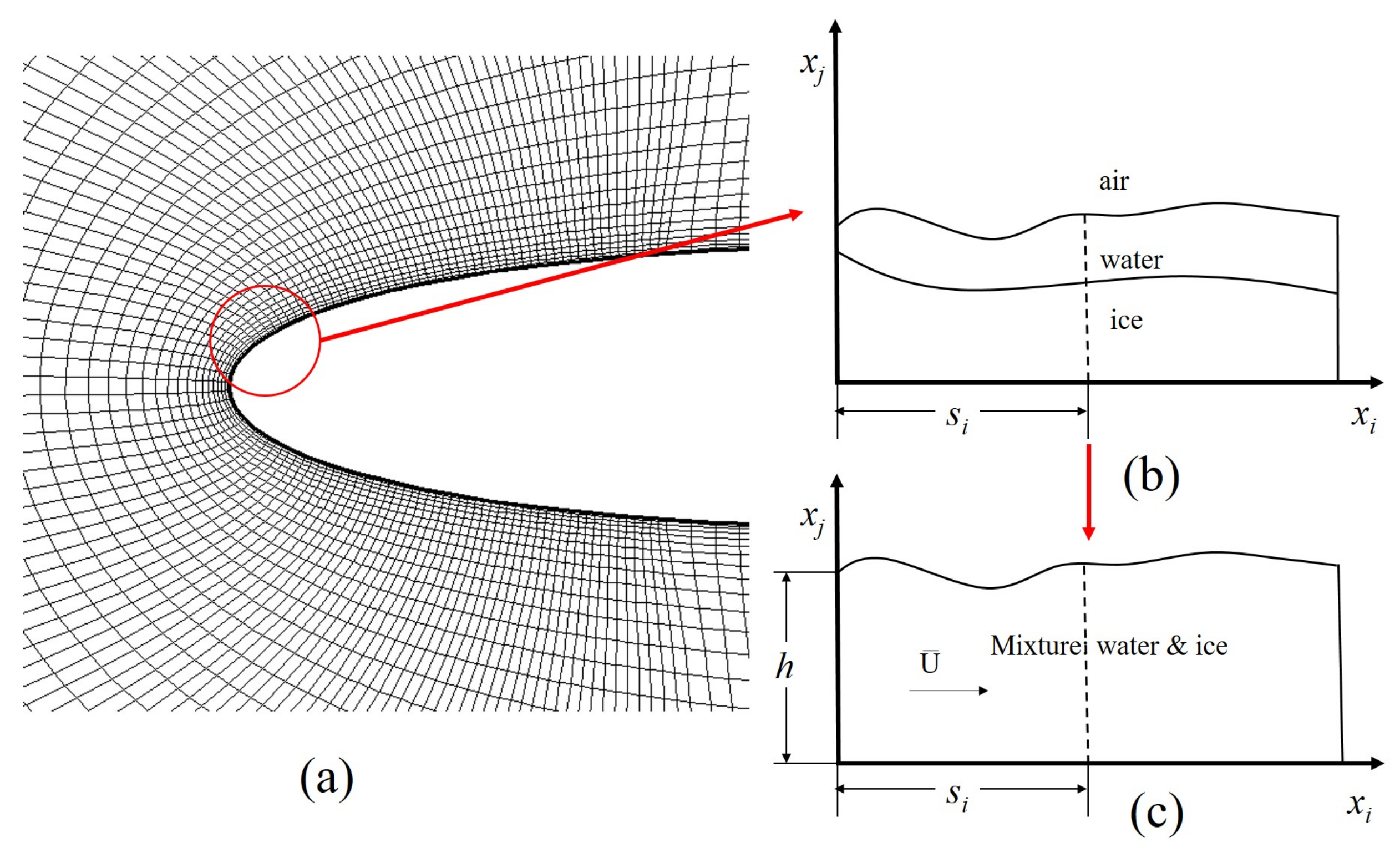
Source Image: mdpi.com
Download Image
Earth’s Furnace Is Ideal for Life – Reasons to Believe What is the difference between condensation and accretion? 13. Describe the planetesimal theory of planet formation. 14. How does the planetesimal theory of planet formation explain the asteroids? 15. How did the craters we see on many of the planets form? 16.

Source Image: reasons.org
Download Image
Large Gas-Phase Source of Esters and Other Accretion Products in the Atmosphere | Journal of the American Chemical Society Nov 21, 2023Accretion is the gradual accumulation of solid materials due to gravitational forces.In the accretion process, gas and dust are attracted by gravitational forces to form a central collection of

Source Image: pubs.acs.org
Download Image
Large Gas-Phase Source of Esters and Other Accretion Products in the Atmosphere | Journal of the American Chemical Society What is the difference between condensation and accretion? Solution Summary: The author explains the difference between condensation and accretion. Condensation is the first process of planet formation where solid grains are formed depending on the temperature of the region.

Source Image: pubs.acs.org
Download Image
Types Of Accretion And Their Efficiency Rates – FasterCapital
Large Gas-Phase Source of Esters and Other Accretion Products in the Atmosphere | Journal of the American Chemical Society The condensation sequence is the sequence by which different kinds of material condense out of the solar nebula based on the distance from the sun and decreasing temperature.
Applied Sciences | Free Full-Text | A New Ice Accretion Model for Aircraft Icing Based on Phase-Field Method Large Gas-Phase Source of Esters and Other Accretion Products in the Atmosphere | Journal of the American Chemical Society What is the difference between condensation and accretion? 13. Describe the planetesimal theory of planet formation. 14. How does the planetesimal theory of planet formation explain the asteroids? 15. How did the craters we see on many of the planets form? 16.