The ADNA structure. A-DNA is one of the possible double helical structures which DNA can adopt. A-DNA is thought to be one of three biologically active double helical structures along with B-DNA and Z-DNA.It is a right-handed double helix fairly similar to the more common B-DNA form, but with a shorter, more compact helical structure whose base pairs are not perpendicular to the helix-axis as
Do you know what DNA is and its functions and structure?
The components of DNA From the work of biochemist Phoebus Levene and others, scientists in Watson and Crick’s time knew that DNA was composed of subunits called nucleotides 1 . A nucleotide is made up of a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) or cytosine (C).
Source Image: freepik.com
Download Image
5 days agoDefinition. Deoxyribonucleic acid (abbreviated DNA) is the molecule that carries genetic information for the development and functioning of an organism. DNA is made of two linked strands that wind around each other to resemble a twisted ladder — a shape known as a double helix. Each strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar (deoxyribose

Source Image: freepik.com
Download Image
DNA explained: Structure, function, and impact on health Dec 16, 2023DNA is a linear biopolymer, a compound biomolecule in the form of a double helix. Polymers are made of monomers, and in DNA, these monomers are called nucleotides or nucleobases. The enzymes
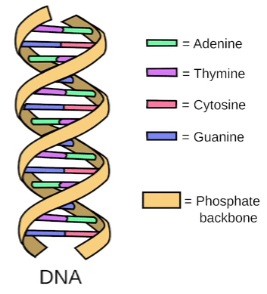
Source Image: mometrix.com
Download Image
What Does The A In Dna Stand For
Dec 16, 2023DNA is a linear biopolymer, a compound biomolecule in the form of a double helix. Polymers are made of monomers, and in DNA, these monomers are called nucleotides or nucleobases. The enzymes What does DNA look like? Your DNA structure is made up of four base pairs: adenine (A), cytosine (C), thymine (T), and guanine (G). The bases form pairs (base pairs); A with T and C with G. The base pairs connect with a sugar molecule and a phosphate molecule (making a nucleotide) that form a spiral staircase (double helix). The base pairs are
What is DNA? – Comprehensive Biology Review (Video)
Deoxyribonucleic acid ( / diːˈɒksɪˌraɪboʊnjuːˌkliːɪk, – ˌkleɪ -/ ⓘ; [1] DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of all known organisms and many viruses. Gene Editing: Group Says OK Do It, But Be Careful
Source Image: nbcnews.com
Download Image
Where are Your DNA, Chromosomes, and Genes? Diagram | Chromosome, Genetics activities, Genetics traits Deoxyribonucleic acid ( / diːˈɒksɪˌraɪboʊnjuːˌkliːɪk, – ˌkleɪ -/ ⓘ; [1] DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of all known organisms and many viruses.

Source Image: pinterest.com
Download Image
Do you know what DNA is and its functions and structure? The ADNA structure. A-DNA is one of the possible double helical structures which DNA can adopt. A-DNA is thought to be one of three biologically active double helical structures along with B-DNA and Z-DNA.It is a right-handed double helix fairly similar to the more common B-DNA form, but with a shorter, more compact helical structure whose base pairs are not perpendicular to the helix-axis as

Source Image: adntro.com
Download Image
DNA explained: Structure, function, and impact on health 5 days agoDefinition. Deoxyribonucleic acid (abbreviated DNA) is the molecule that carries genetic information for the development and functioning of an organism. DNA is made of two linked strands that wind around each other to resemble a twisted ladder — a shape known as a double helix. Each strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar (deoxyribose

Source Image: medicalnewstoday.com
Download Image
Pin on Abstract Art Canvas Prints Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a molecule that contains the biological instructions that make each species unique. DNA, along with the instructions it contains, is passed from adult organisms to their offspring during reproduction. Where is DNA found? In organisms called eukaryotes, DNA is found inside a special area of the cell called the nucleus.

Source Image: pinterest.com
Download Image
What does DNA stand for? Learn more about this important molecule! Dec 16, 2023DNA is a linear biopolymer, a compound biomolecule in the form of a double helix. Polymers are made of monomers, and in DNA, these monomers are called nucleotides or nucleobases. The enzymes
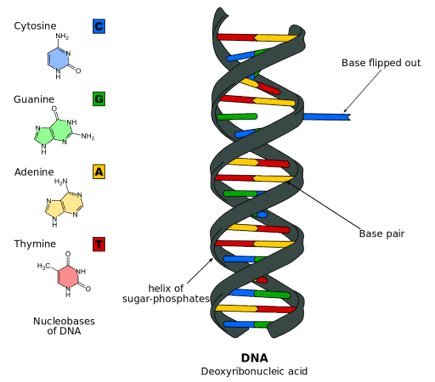
Source Image: nebula.org
Download Image
Aya Kachi on X: “Science 🧬” / X What does DNA look like? Your DNA structure is made up of four base pairs: adenine (A), cytosine (C), thymine (T), and guanine (G). The bases form pairs (base pairs); A with T and C with G. The base pairs connect with a sugar molecule and a phosphate molecule (making a nucleotide) that form a spiral staircase (double helix). The base pairs are

Source Image: twitter.com
Download Image
Where are Your DNA, Chromosomes, and Genes? Diagram | Chromosome, Genetics activities, Genetics traits
Aya Kachi on X: “Science 🧬” / X The components of DNA From the work of biochemist Phoebus Levene and others, scientists in Watson and Crick’s time knew that DNA was composed of subunits called nucleotides 1 . A nucleotide is made up of a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) or cytosine (C).
DNA explained: Structure, function, and impact on health What does DNA stand for? Learn more about this important molecule! Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a molecule that contains the biological instructions that make each species unique. DNA, along with the instructions it contains, is passed from adult organisms to their offspring during reproduction. Where is DNA found? In organisms called eukaryotes, DNA is found inside a special area of the cell called the nucleus.